Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Exam01 Stats
Cargado por
me2742700Descripción original:
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Exam01 Stats
Cargado por
me2742700Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
Exam No.
1 Statistics
ME274 – Spring 2009
Curving of grades: We do not curve (normalize) scores on individual exam scores.
Instead we wait until final course scores are known and then set the grade breakpoints
on the final course scores. Typically these breakpoints are close to a straight scale with
some adjustments downward when needed. Do not forget that homeworks, quizzes,
fundamentals exam and blog participation account for 25% of your course grade.
Exam averages: Comparing your exam score with the course average for the exam
does not provide you with a good indication of your performance. Recall that our exam
score weightings are nonlinear (25% and 50% weighting on the lower and higher,
respectively, of the midterm and final exam). If you shoot for an “average” score on your
exam scores, you could easily end up with a course grade lower than a C. People typically
do better on the final exam (since they are seeing the material for the second time).
Because of this, the final ends up with a higher weighting for many in the class. With this
change, the average score on an individual exam loses significance. Having said that,
however, the average (mean) for this exam is 72.2%.
Grade distributions: The better indicators to you on your standing in the class are
the grade distributions on individual problems. These are provided below. Use these to
see how you stand on each problem individually. Try to learn from your mistakes on any
given problem so that you can improve on these topics and not make similar mistakes
when you see them again in future work in the course.
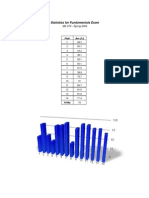
Total number of exams: 235
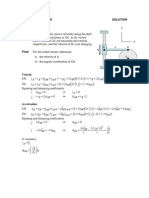
Problem No. 1 grade distribution (20 points max):
18 - 20: 115
16 - 17: 29
14 - 15: 21
12 - 13: 16
12 > 54
Problem No. 2 grade distribution (20 points max):
18 - 20: 128
16 - 17: 32
14 - 15: 20
12 - 13: 23
12 > 32
Problem No. 3 grade distribution (20 points max):
18 - 20: 22
16 - 17: 44
14 - 15: 15
12 - 13: 63
12 > 91
TOTAL exam grade distribution (60 points max):
54 - 60: 36 (15.3%)
48 - 53: 52 (22.1%)
42 - 47: 57 (24.2%)
36 - 41: 41 (17.4%)
36 > 49 (20.9%)
También podría gustarte
- Quiz05 Div3 SolnDocumento1 páginaQuiz05 Div3 Solnme2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- ME 274 - Spring 2009 Solution Quiz No. 4 - Div 3 Monday, February 9Documento1 páginaME 274 - Spring 2009 Solution Quiz No. 4 - Div 3 Monday, February 9me2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- ME 274 - Spring 2009 Solution Quiz No. 4 - Div 1 Monday, February 9Documento1 páginaME 274 - Spring 2009 Solution Quiz No. 4 - Div 1 Monday, February 9me2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- Quiz05 Div1 SolnDocumento1 páginaQuiz05 Div1 Solnme2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- Exam01 SolnDocumento5 páginasExam01 Solnme2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- Particle KineticsDocumento20 páginasParticle Kineticsme2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- Exam01 CoverDocumento2 páginasExam01 Coverme2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- Quiz02 Div1 SolnDocumento1 páginaQuiz02 Div1 Solnme2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- Quiz03 Div3 SolnDocumento2 páginasQuiz03 Div3 Solnme2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- Quiz03 Div1 SolnDocumento2 páginasQuiz03 Div1 Solnme2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- FE StatisticsDocumento1 páginaFE Statisticsme2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- Quiz02 Div3 SolnDocumento1 páginaQuiz02 Div3 Solnme2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- Quiz01 Div3 SolnDocumento1 páginaQuiz01 Div3 Solnme2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- Fundamentals SolnDocumento5 páginasFundamentals Solnme2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- FE CoverDocumento1 páginaFE Coverme2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- Exam InfoDocumento1 páginaExam Infome2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- First Day Sp09Documento1 páginaFirst Day Sp09me2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- Sample ExamsDocumento24 páginasSample Examsme2742700100% (1)
- Dynamics Fundamentals: Mathematics, Vectors and Point KinematicsDocumento18 páginasDynamics Fundamentals: Mathematics, Vectors and Point Kinematicsme2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- KinematicsDocumento27 páginasKinematicsme2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- Syllabus Sp09Documento2 páginasSyllabus Sp09me2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- Homework FormatDocumento1 páginaHomework Formatme2742700Aún no hay calificaciones
- ME 274 - Fall 2008 Solution Final Examination Problem No. 1 GivenDocumento16 páginasME 274 - Fall 2008 Solution Final Examination Problem No. 1 Givenme2749529Aún no hay calificaciones
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (120)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2101)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- French Preap and Ap SyllabusDocumento5 páginasFrench Preap and Ap Syllabusapi-177128821Aún no hay calificaciones
- Muktha Swadhyaya Peetham Rashtriya Sanskrit Sansthan: (Details Regarding Admission / Eligibility Criteria)Documento2 páginasMuktha Swadhyaya Peetham Rashtriya Sanskrit Sansthan: (Details Regarding Admission / Eligibility Criteria)Mitra PathakAún no hay calificaciones
- Randi JohnsonDocumento2 páginasRandi Johnsonapi-253981743Aún no hay calificaciones
- DLL Arts Q3 W6Documento7 páginasDLL Arts Q3 W6Cherry Cervantes HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Communication Is Simply The Act of Transferring Information From One Place, Person or Group To AnotherDocumento3 páginasCommunication Is Simply The Act of Transferring Information From One Place, Person or Group To AnotherYram GambzAún no hay calificaciones
- Dissertation Overview - Therapeutic Landscaping - Ifrah TanweerDocumento22 páginasDissertation Overview - Therapeutic Landscaping - Ifrah TanweerifrahAún no hay calificaciones
- Group Work 1 1Documento21 páginasGroup Work 1 1hopeboyd36Aún no hay calificaciones
- Delta Module One Pre Interview Task: Name Maria Victoria Mermoz PaciDocumento4 páginasDelta Module One Pre Interview Task: Name Maria Victoria Mermoz PaciMaria Victoria Mermoz PaciAún no hay calificaciones
- William Allan Kritsonis, PHDDocumento35 páginasWilliam Allan Kritsonis, PHDWilliam Allan Kritsonis, PhDAún no hay calificaciones
- How To Pass The Board Exam 101Documento1 páginaHow To Pass The Board Exam 101Kendra Joy SendicoAún no hay calificaciones
- Sining Silabus AgricultureDocumento11 páginasSining Silabus AgricultureJudemarife RicoroyoAún no hay calificaciones
- Module 6Documento16 páginasModule 6mahreen habibAún no hay calificaciones
- Reading Intervention Action Plan For Frustration and Non-Readers SY 2020-2021Documento2 páginasReading Intervention Action Plan For Frustration and Non-Readers SY 2020-2021December Cool100% (1)
- Theeffectsoftechnologyonyoungchildren 2Documento5 páginasTheeffectsoftechnologyonyoungchildren 2api-355618075Aún no hay calificaciones
- ComeniusDocumento38 páginasComeniusDora ElenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Assessment 2 Brief: Subject Code and Title Assessment Individual/Group Length Learning OutcomesDocumento5 páginasAssessment 2 Brief: Subject Code and Title Assessment Individual/Group Length Learning OutcomesbhavikaAún no hay calificaciones
- What's Up? - Part 1: AL Answers 66 Questions To Enlighten Us About Body, Mind and Spirit.Documento176 páginasWhat's Up? - Part 1: AL Answers 66 Questions To Enlighten Us About Body, Mind and Spirit.Marcus RobbinsAún no hay calificaciones
- Competency 9 Powerpoint VoiceoverDocumento17 páginasCompetency 9 Powerpoint Voiceoverapi-693321754Aún no hay calificaciones
- Disease Prediction Using Machine Learning: December 2020Documento5 páginasDisease Prediction Using Machine Learning: December 2020Ya'u NuhuAún no hay calificaciones
- Eclectic Approach in Teaching EnglishDocumento5 páginasEclectic Approach in Teaching EnglishPapua NetAún no hay calificaciones
- UTSDocumento2 páginasUTSEverlyne SiloyAún no hay calificaciones
- PerDev ReviewerDocumento4 páginasPerDev ReviewerJaira PedritaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Looking Glass Self BotanywaybootDocumento1 páginaThe Looking Glass Self BotanywaybootRanie MonteclaroAún no hay calificaciones
- Customer-Centric Companies Are 60% More Profitable!Documento1 páginaCustomer-Centric Companies Are 60% More Profitable!Pham Van ThanhAún no hay calificaciones
- Arminda Nira Hernández Castellano OLLDocumento19 páginasArminda Nira Hernández Castellano OLLArminda NiraAún no hay calificaciones
- Pdve PaperDocumento2 páginasPdve Paperjimaerospace05Aún no hay calificaciones
- What Is Trauma?Documento10 páginasWhat Is Trauma?gayle livelo100% (1)
- Abstract Subtle Effect of Sanskrit Text and Script Compared To Other Languages PDFDocumento2 páginasAbstract Subtle Effect of Sanskrit Text and Script Compared To Other Languages PDFNikolaAún no hay calificaciones
- 10 Brain Hacks To Learn Fast With Jim Kwik - WorkbookDocumento12 páginas10 Brain Hacks To Learn Fast With Jim Kwik - WorkbookManpreet Singh69% (13)
- ABCE PHD Studentship Application FormDocumento4 páginasABCE PHD Studentship Application Formnasibeh tabriziAún no hay calificaciones